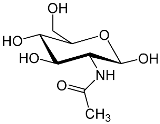
 After proteins and nucleic acids, carbohydrates play an important role in the functioning of a cell. Apart from being a fuel for cells, carbohydrate interaction with protein plays an important role in cell adhesion, signal transduction, host-pathogen recognition and inflammation. A major carbohydrate/glyconutrient (N-acetyl-glucosamine) is an important part of connective tissue, which holds the cells together. There are several hundred glyconutrients are present in the human body. Researchers have pinpointed only eight as essential glyconutrient and N-acetyl-glucosamine is one of them. (N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, or GlcNAc, or NAG) is a monosaccharide derivate of glucose. NAG is formed by an amide bond between glucosamine and acetic acid. The molecular formula of NAG is C8H15O6 and a molar mass of 221.21 g/mol. In bacteria NAG is present as a structural unit in cell wall. NAG crosslink with N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNac) to for a layered structure called peptidoglycan, which is an integral component of bacterial cell wall. Itís also present in outer covering of insects and crustaceans in the form of a polymer chitin. | In humans N-acetyl-glucosamine is of paramount importance. NAG helps in the repair of cartilage, its decreases pain and inflammation with bones joints. Glucosamine a metabolic byproduct of NAG helps mend mucosal lining. It also plays role in tissue rebuilding as well as digestive tract. Presence of NAG in brains helps in the functioning of nervous system and enhances learning process. Glucosamine receptors help in the transport of thyroglobulin. Its presence in lever helps in the control secretion of insulin. N-acetyl-Glucosamine is known to have anti-viral and anti-tumor activity. This sugar helps in preventing the spread of influenza virus, herpes virus and tumors. A reduced level of N-acetyl-Glucosamine has been observed in colon cancer patients. When Glucosamine, glyconutrients and mannose were added to drinking water of mice, it stopped the growth of Ehrlich ascites tumor. Decrease amount of N-acetyl glucosamine is known to cause crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and diseases of bowel and bladder. | Protein N-acetyl-glucosamine interaction plays an important role in the functioning of a cell. Studying protein-NAG interaction is important problem in the field of molecular recognition. Doing experiment to find NAG interacting protein is time consuming, difficult and costly. In silico techniques are less time consuming and easy to perform. In past, a number of computational methods have been developed to predict carbohydrate-protein interaction sites. Ahmed et al, use a 3D structure approach to develop a common method for the prediction of carbohydrate binding site. They were able to achieve 87% sensitivity and 23% specificity using a neural network prediction method. Ahmed et al also develop a method for the prediction of galactose binding site, with 63% sensitivity and 79% specificity. Thornton et al predicted carbohydrate-binding site with overall accuracy of 65%. The accuracy increases to 87% for carbohydrate-binding enzymes. Balaji et al developed a program COTRAN to predict galactose binding site. The overall performance of program over six folds is 0.71 specificity and 0.76 sensitivity. All the above are 3D structure based method. None of the above method is developed specifically to predict the NAG-protein interaction sites. The major limitation of the above methods is that you need to have 3D structure of your query sequence. | ||

- Home
- |About
- |Algorithm
- |Developers
- |Contact
- |Help
- |Data
- |Standalone