|
ccPDB is a database of datasets compiled from literature and Protein Data Bank (PDB). It allow users to compile desired dataset from PDB. A number of tools have been integrated to facilitate PDB users.This page is designed for providing help on ccPDB. Please click on topic or subtopic for detail help.
We have collected and compiled datasets from published literature after extensive search. These datasets were orignally derived from Protein Data Bank (PDB) and used for developing prediction methods. In order to facilitate users, we are maintain local copy of these datasets as well as reference and link to original site.
Go to Top
This page maintain datasets compiled from latest release of PDB (31st January 2012). These datasets were generated using commonly used standard protocols like non-redundant chains, structures solved at high resolution. Structure datasets from 31st January are complied using non-redundant protein chains from bc-30 (level of redundancy is 30%). The list can be downloaded from ftp://resources.rcsb.org/sequence/clusters/. Datasets of DNA/RNA and ligand/metals are complied using blast-clust at 25% redundancy. All datasets includes description on their top that include how these datasets were compiled. Following examples provides detail description of datasets.
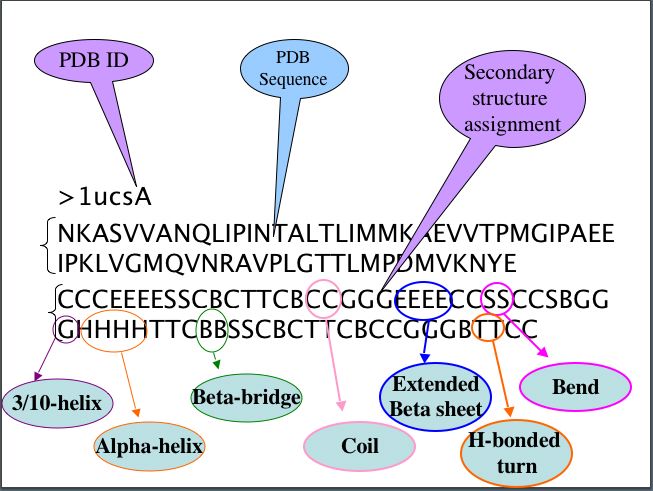
1. Description of datasets of regular secondary structure:
This dataset was created using DSSP and PDB_select. There are three line for each PDB ID, First line is PDB ID with chain, Second is amino acid sequence in single letter code and third line is secondary structure states.
H, E and C secondary structure at each amino acid residue corresponding to amino acid of respective PDB sequence, where,
H=Alpha helix, B= Beta bridge, E=Extended beta sheet, G=3/10 helix, I=pi helix,
T=hydrogen bonded turn,
S=bend,C=coil.
For example: Regular secondary structure is assigned as follow-
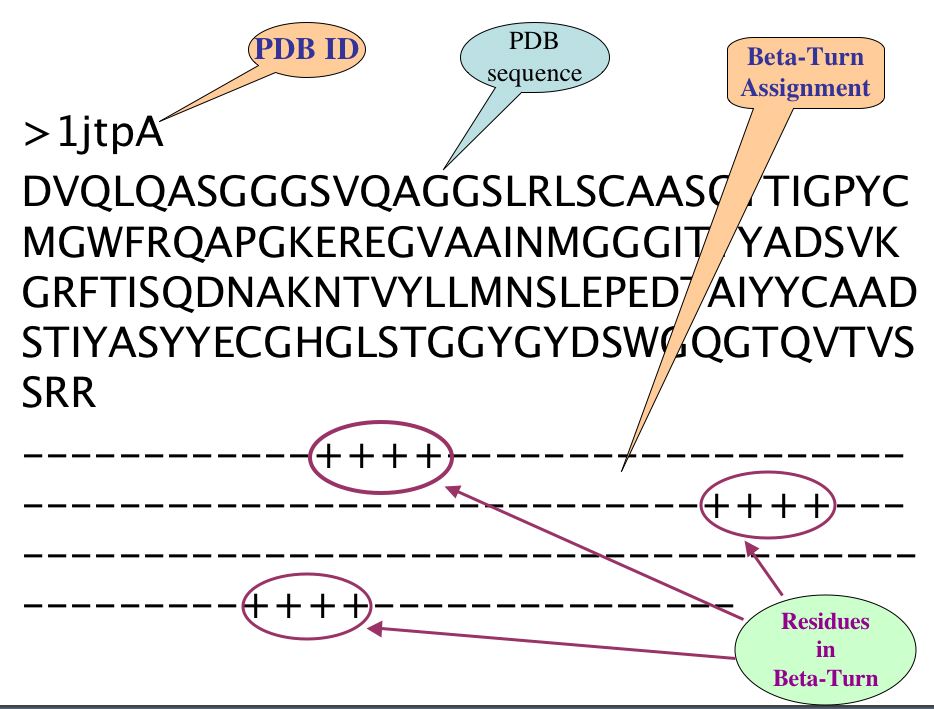
2. Description of irregular secondary structure dataset:
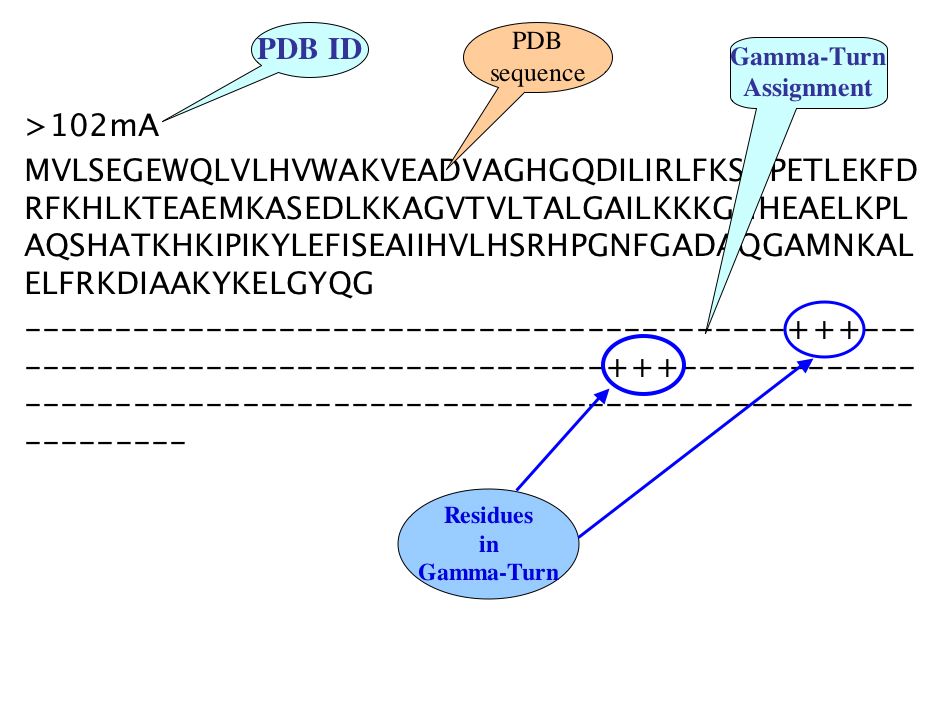
There are three line in each PDB of irregular secondary structure compiled datasets, First line is PDB ID with chain, Second is FASTA sequence and third line is assignment of specific Turn at each amino acid residue corresponding to amino acid of respective PDB sequence, where plus (+) sign indicate the corresponding amino acid occur in Specific Turn while sign(-) indicates non Turn amino acid residues.
For example: Beta-Turn assigned as follow-
For example: Gamma-Turn assigned as follow-
Go to Top
Online submission is important for maintaining datasets upto-date. Though we will make our best effort to maintain all datasets published in literature but it is not possible without cooperation of community. This page allows scientific community to submit new datasets to our database. Please note we only maintain datasets which has been used in scientific publications.
Go to Top
This is important module for creating customized datasets. In order to provide flexibility, we developed six sub-module for creating customized datasets-
| Sub-modules | Description with example |
|---|
| Proteins/Chains | This allow users to create a set of proteins have desired function. For example user can create set of ATP binding proteins from PDB (See example ATP binding proteins). |
| General filters | Filter proteins from PDB having desired resolution, length of proteins etc. For example you may create set of non-redundant (cut-off 30%) proteins where structure was determine by X-ray crystallography at resolution better than 2.0 Angstrom having number of residues between 50 to 300 (See example non-redundant proteins). |
| Combine sets | This option allows users to generate new set of PDB chains from two sets of PDB chains using various combinations. User may create unique PDB IDs from ATP binding and non-redundant proteins (See example Combined Sequences). |
| Extract sequences | Extract the sequences of selected PDB chains from PDB. For example protein sequences can be extracted from PDB for for set of ATP binding proteins (See example ATP sequences for ATP binding proteins) |
| Non-redundant sequences | This module allows users to create non-redundant set of proteins form set of proteins. Here we used blastclust for generating set of non-redundant proteins (See non-redundant atp binding protein sequences). |
| Annotation of residues | This module allows to assign function of each residue in selected set of proteins. This function may be interacting residue or specific structure. For example ATP interacting residues can be assigned in ATP binding proteins (See ATP interacting residues in ATP binding proteins) |
| | | |
Detail description of each step is given below-
This step allows user to extract PDB chains of desired properties like interacting residues in proteins (e.g., DNA,RNA,ATP, NAG, MG). It also allows to extract proteins based on their their secondary structure like helix, sheet, beta-turn, bulges. Users have option to extract proteins from PDB or from set of PDB IDs.
| Type of Dataset | Description of set of proteins/chains |
|---|
| Regular Secondary Structure | This option allows users to create set of proteins having desired content of secondary structure states (secondary structures states were assigned using DSSP). |
| Irregular Secondary Structure | This option allows users to create datasets related to irregular secondary structures. For example user can extract protein chains from PDB having b-turns or gamma-turns. Promotif is used for assigning most of turns and their types. |
| Small Nucleotides Interaction | Generate set of proteins which interact with small nucleotides like ATP, GTP, ADP, GMP. For example user can extract ATP binding proteins. LPC is used to for assigning nucleotide interacting residues in proteins. |
| DNA Interactions | This option allows to extract DNA binding proteins. It also allow users to extract proteins which interact specific type of amino acid. |
| RNA Interactions | RNA binding proteins can be extracted using this option. |
| Ligand Interactions | Allows user to extract ligand binding proteins |
| Metal Interactions | User can extract metal binding proteins using this option |
| Specific domain | Create set of proteins having specific type of domain |
| Physical properties | Proteins having desired physico-chemical properties |
| Amino acid composition | Extract PDB chains having specific amino acid composition |
Go to Top
These filters allows users to extract chains from PDB that satisfy their conditions. Following are main options in this module.
| Options | Description |
|---|
| Experimental method | User may select experimental method used to determine structure of proteins. Their are three options, i) Any for all structure in PDB, ii) X-Ray for structure solved by X-ray crystallography and iii) NMR for NMR solved structures. By default option Any is selected |
| Select Organism | User may enter name of organism for searching PDB from that organism only, by default ALL is selected. Enter HOMO SAPIENS for extracting human proteins from PDB |
| Resolution Range | Allow users to select protein whoes structure solved at given resolution. |
| Number of Amino Acids | Option allow to select proteins having number of residue in desired range. |
| Select level of redundancy | User may select level of redundancy like 30, 40, 90 for filtering redundant or similar proteins, 40 means all proteins having sequence similarity more than 40% will be filtered. By default "No Redundancy", all proteins are considered (no filtering of redundant proteins). |
Go to Top
This option allows users to generate new set of PDB chains from two sets of PDB chains using various combinations. For example it allows users to select chains, which are common in two sets, or unique chains in two sets.
Go to Top
Above three steps allows users to extract PDB chains as per users requirement. This step allows users to extract amino acid sequence of PDB chains extracted from above steps. Input of this module is list of PDB IDs, each ID in new line. User can also submit PDB chains where four character of PDB ID should be lowercase and PDB chain should be in uppercase, eg. 1y04A.
Go to Top
In order to create any dataset, non-redundant protein sequences are required. In this step redundant protein are removed from a given set of proteins. This option and above four steps allows user to create desired dataset of proteins, which can be used to develop method for predicting function at protein level. In Non-redundant data page user can remove redundant protein sequences from 25% to 90% using BlastClust package.
Go to Top
This step allows user to assign the function of each residue in a protein. For example user can assign secondary structure of each residue of a protein. Similarly protein residues that interact with different types of ligand like DNA, RNA, ATP, metal can be assigned using this module. This option is important for developing prediction method at residue level.
This module require a list of PDB chain IDs (eg. 1bcpA, where four PDB character should be in lowercase and chain should be in uppercase).
Go to Top
| Web Services |
| We have provided following web services in ccPDB |
In past number of web servers have been developed to extract useful information from tertiary structure. These servers allows users to perform anlysis on their structure (PDB ID). These servers are scattered on Internet, it very difficult for users to use their potentials. We collected more than 40 servers from literature and developed a meta server, where user can submit PDB ID once and can got information about PDB ID from any of these server.
Go to Top
This page allow users to perform similarity search against PDB using BLAST. In this page user can submit their sequence in fasta format to run blast. User can select desired weight matrix (e.g., BLOSUM62, BLOSUM80,PAM30) and e-value.
Go to Top
This page is designed for extracting structural information about a protein (PDB ID). Following type of information is extracted from protein i) amino acid composition, ii) composition of functional residues (e.g., charge, polar), iii) secondary structure content, iv) ligands interacting residues and v) frequency of irregular secondary structure states (e.g., alpha, beta, gamma turns).
Go to Top
This option allows users to search PDB on major fields. This have following options for searching and displaying result.
Select fields to be Searched
|
|---|
| Option | Description |
|---|
| All | Search in any field of PDB (by default) |
| PDB ID | Select this option for searching PDB IDs |
| Ligands | User can search ligand binding proteins |
| Domain present | Search desired domain in protein structures |
| Organism | Option for searching organism |
| Metals | Important for searching metal binding proteins |
| Select fields to be displayed |
|---|
| Option | Description of fields |
| Amino acid composition | Allow to display amino acid composition of proteins |
| Physico-chemical property | Display composition of specific group of residues like polar, hydrophobic, charged residues. |
| Beta turns | Display beta-turns in proteins |
| Gamma turns | Display gamma-turn in proteins |
| Buldges | Allow to display buldges in proteins |
| Secondary structure | Secondary structure of proteins can be displayed |
| Ligands | Display ligands in ligand binding structures |
| Domains | Display domains in structures |
Go to Top
In order to develop a prediction method one need to create patterns from proteins that can be read by machine learning techniques. Their are number of software packages like SVM_light, SNNS, Weka that allows to implement many machine learning techniques like support vector machine (SVM), artificial neural network (ANN). In order to provide facility to bioinformaticians particularly students or new developers, we developed facility to generate patterns of desired window size and in desired format (e.g., SVM, SNNS, Weka). This module have two subroutine, first for creating patterns at residue level and second for creating pattern at protein level. Following are options for both types of module.
Options for creating patterns at residue level
| Option | Detail description of option |
|---|
| Window Length | For creating overlapping amino acid patterns from proteins. For example window length 17, it will generate patterns of 17 residues like 1 to 17, 2 to 18, 3 to 19. |
| Type of Pattern | This allow this three options, i) residue composition will calculate amino acid composition of each pattern (a vector of dimension 20),ii) similarily dipeptide composition will compute dipeptide composition of each peptide (a vector of dimension 400) and iii) binary profile will represent a residue by a vector of 20 |
| Software Package | Allows user to generate pattern by vector/matrix suitable to any of three packages i) SVM_light a package for implementing SVM, ii) SNNS a package for implementing ANN and iii) Weka for implementing various machine learning techniques. |
| Negative patterns | A pattern having having central residue functional is called positive pattern and rest of residues are called negative patterns. In general negative patterns are more than positive patterns in a protein. This option allows user to select negative pattern equal to positive patterns. |
Options for creating patterns at protein level
| Option | Detail description of option |
|---|
| Type of Pattern | This allow this three options, i) residue composition will calculate amino acid composition of each pattern (a vector of dimension 20),ii) similarily dipeptide composition will compute dipeptide composition of each peptide (a vector of dimension 400) and iii) binary profile will repersent a residue by a vector of 20 |
| Software Package | Allows user to generate pattern by vector/matrix suitable to any of three packages i) SVM_light a package for implementing SVM, ii) SNNS a package for implementing ANN and iii) Weka for implementing various machine learning techniques. |
Go to Top
This server allows users to download PDB files from latest release of PDB. In addition it also allows users to download various types of information of PDB files that includes dssp files, dihedral angles, surface accessibility and hydrogen bonds.
| Select type of information you wish to download |
|---|
| Option | Type of information |
|---|
| PDB files | This allows users to download PDB files. The Protein Data Bank (PDB) file contains the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids. |
| DSSP | This provides download facilities of DSSP files. DSSP assigned secondary structure information where 'H' for helix, 'E' for beta sheet and 'C' for coil. |
| PDBFINDER2 | This allows users to download PDBFINDER2 file. |
PDBFINDER2 file contains following informations:|
| Type of information | Description of specific information of PDBFINDER2 file. |
|---|
| Access | Access is a relative side chain accessibility, where 0=buried, 9=exposed. |
| Angles | In angles information, Absolute Z-score of the largest angle deviation per residue (using Engh&Huber parameters), absolute Z-Scores in the range [5..2] are mapped to [0..9].) |
| Backbone | Protein backbone information is a number of similar backbone conformations found in the database, numbers in the range [0..10] are mapped to [0..9]. |
| Bonds | In bonds information absolute Z-score of the largest bond deviation per residue (using Engh&Huber parameters), absolute Z-Scores in the range [5..2] are mapped to [0..9]. |
| Bumps | This information includes sum of bumps per residue, distances in the range [0.1 .. 0] are mapped to [0..9]. |
| Cons-Weight | Cons-Weight is the HSSP conservation weights, multiplied with 9. |
| Cryst-Cont | In this information '+' marks residues involved in crystal contacts. |
| Entropy | The HSSP entropy, multiplied with 9/ln(20). |
| Flips | This information indicates flipped Asn/Gln/His sidechain, 9=OK, 0=needs flipping. |
| H-Bonds | In this information 9 minus number of unsatisfied hydrogen bonds, an additional 1 is subtracted for a buried backbone nitrogen, 4 for buried sidechain. |
| Inout | It is absolute inside/outside distribution Z-score per residue, Z-scores in the range [4..2] are mapped to [0..9]. |
| Nalign | This information contains number of alignments in the HSSP file on a logarithmic scale: calculate 10^((N-1)*0.25) to get an estimate (N is in [0..9]). The number on the right side is the average number of HSSP alignments per residue. |
| Nindel | It is sum of insertions and deletions, on the same logarithmic scale as Nalign. Again the number on the right is the non-logarithmic average over all residues. |
| Packing-1 | First packing quality Z-score, Z-scores in the range [-5..+5] are mapped to [0..9]. |
| Packing-2 | This is Packing-2 download option. Second packing quality Z-score, Z-scores in the range [-3..+3] are mapped to [0..9]. |
| Peptide-Pl | In this information, RMS distance of the backbone oxygen from the oxygen in similar backbone conformations found in the database, distances in the range [3..1] are mapped to [0..9]. If less than 10 hits are found, there are not sufficient data to perform the following two checks. |
| Phi/Psi | Ramachandran Z-score per residue, Z-Scores in the range [-4..+4] are mapped to [0..9]. |
| Planarity | Z-score for the planarity of the residue sidechain, Z-Scores in the range [6..2] are mapped to [0..9]. Residues without planar side-chains score '9'. |
| Present | This allows to download Present information. It is 9 minus the number of missing atoms per residue. |
| Rotamer | Probability that the sidechain rotamer (chi-1 only) is correct, probabilities in the range [0.1 .. 0.9] are mapped to [0..9]. Gly, Ala and Pro always score '9'. |
| Torsions | Average Z-score of the torsion angles per residue, Z-Scores in the range [-3..+3] are mapped to [0..9]. |
| Chi-1/chi-2 | Z-score for the sidechain chi-1/chi-2 combination, Z-scores in the range [-4..+4] are mapped to [0..9]. Residues with only <=1 side-chain torsion angle score '9'. |
|

