AVP-PEpred: Antiviral Peptide-Percent Efficacy Predictor

How to use
AVP-PEpred Input
AVP-PEpred submit: AVP-PEpred is an online, open source server to predict the quantitative efficacy of input peptides against viruses in terms of percent inhibition values. Its highly user-friendly interface allows the user to simply paste the sequences in FASTA format in the text area on "Predict" page. Load example link loads the example peptides. Two machine learning techniques viz. SVM (Support vector machine) and RF (Random forest)can be selected for making predictions. User can either select any of them or keep the default settings.User can then choose the desired model (e.g. Amino acid composition, binary profile, physicochemical properties, Hybrid etc.) based on which the predictions will be made. Clicking on Run Prediction will predict the percent inhibition values of the user defined peptides.

AVP-PEpred Output
The results are displayed as a table having 7 columns. The first three columns are the Fasta Id, Sequence and its Length. Rest of the columns (4-7) displays the calculated results for input sequences viz. Motifs, predicted values from SVM, predicted values from RF and physicochemical properties of peptides respectively . All the columns of the table have been provided with a sorting functionality. Search functionality is also provided to filter the results.
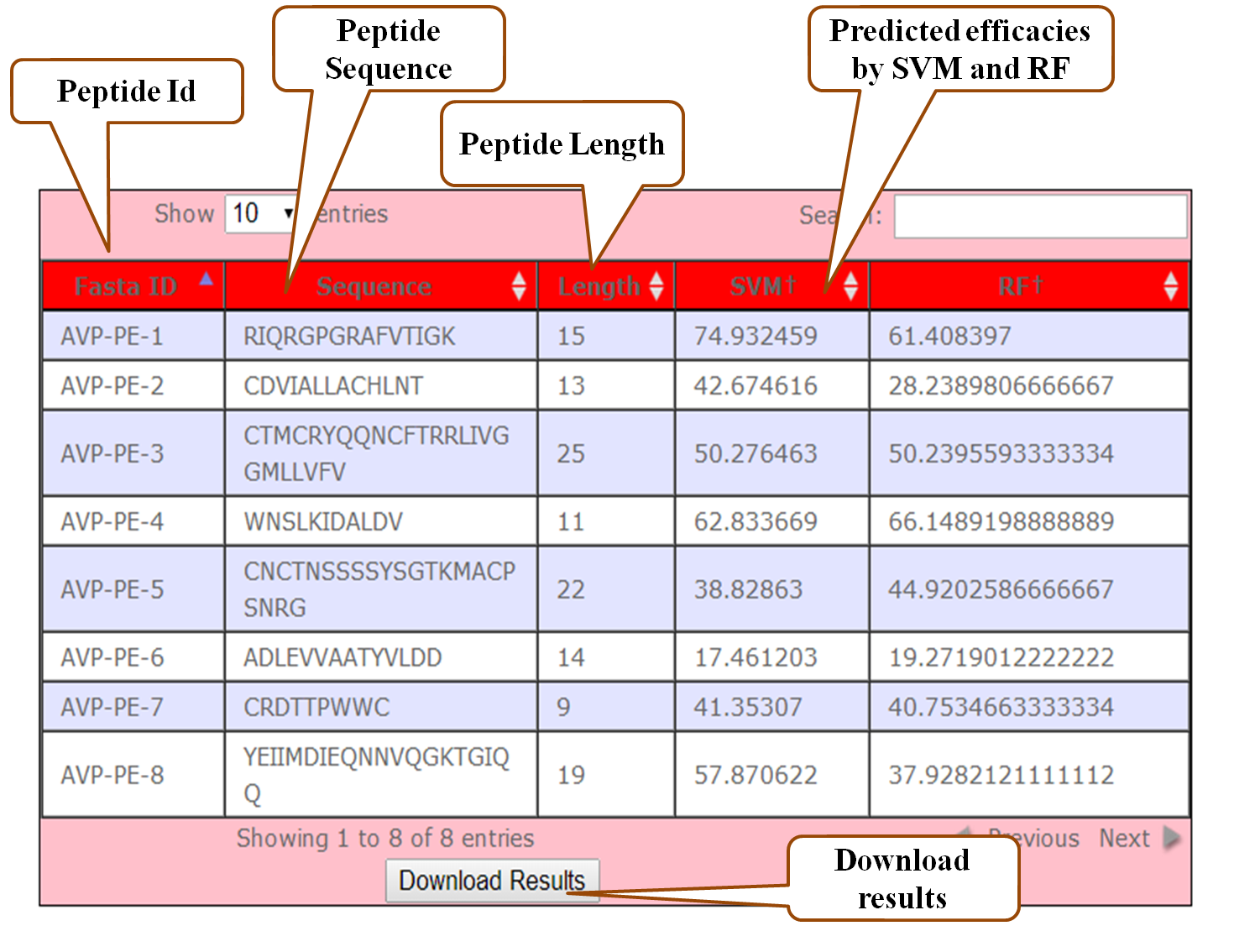
Result interpretation
The percent inhibition value of a peptide denotes its inherent capacity to inhibit or block viral infection. E.g. a peptide showing percent efficacy of 80% signifies that the particular peptide is 80% effective in blocking viral processes. Similarly, the percent inhibition value of 30% shows that a peptide is 30% efficient. The results in the above output may be divided into four groups, for reasons of convenience, as per the predicted percent inhibition values as:
Tools
Apart from predicting the efficacy of peptide in question, we have also provided few tools that can help the users to design novel AVPs and analyze their properties:
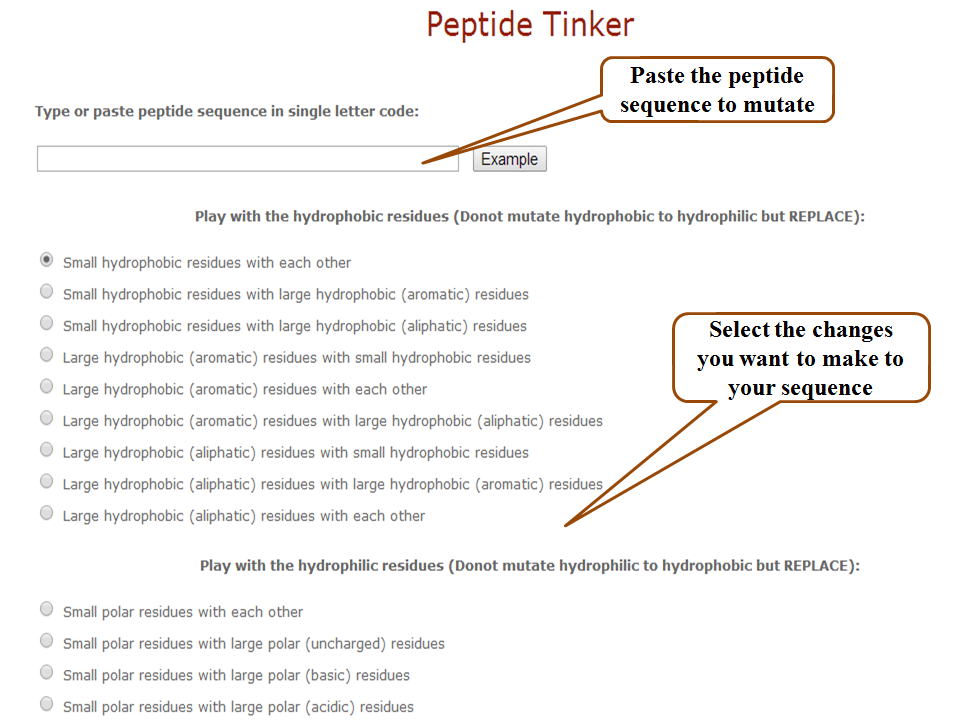
a) Mutation modules: Peptide tinker
This tool is an in-silico counterpart of directed mutagenesis. It allows the user to design new peptide sequences by tinkering only the residues having similar properties say hydrophobic, hydrophilic, aromatic, aliphatic etc. without changing other residues. For this purpose, amino acids have been divided into 7 categories as shown in Supplementary Table S4 of the main article. User can replace only the small hydrophobic residues with each other or with large aromatic and hydrophobic residues or else with aliphatic and hydrophobic residues etc. On the other hand, if the user has no general idea of which residues to mutate, he or she can choose to generate all possible mutants of a given peptide and then choose from among them, the best performing peptides.
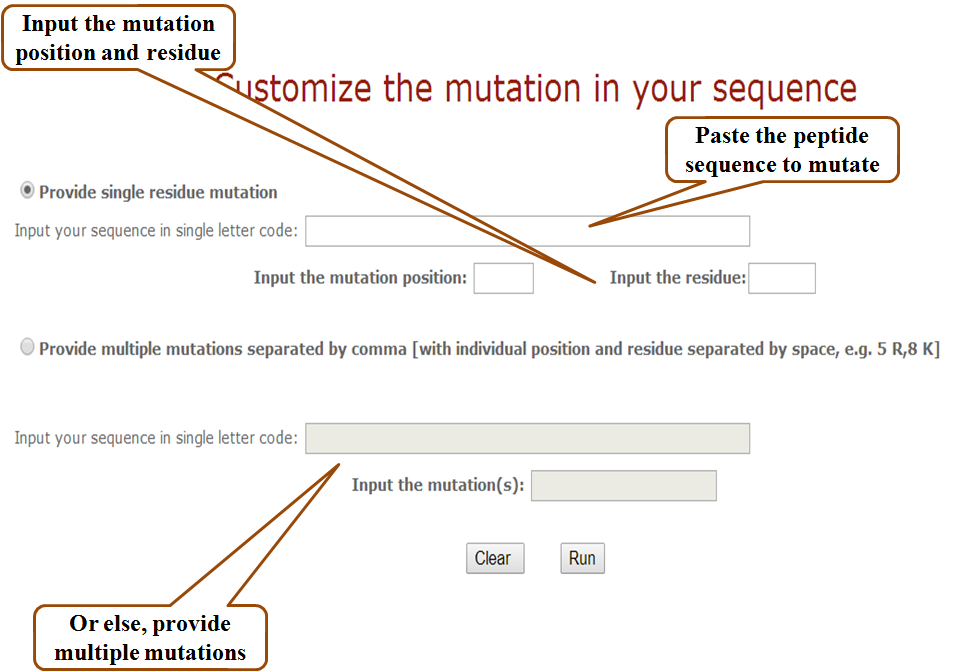
Mutation modules: Custom mutations
We have provided another tool for directed mutagenesis, which allows the user to generate position specific mutants of a given peptide. User can provide the mutation position(s) and the amino acid residue(s) to insert at that position and can then check the efficacy of the resulting peptides.
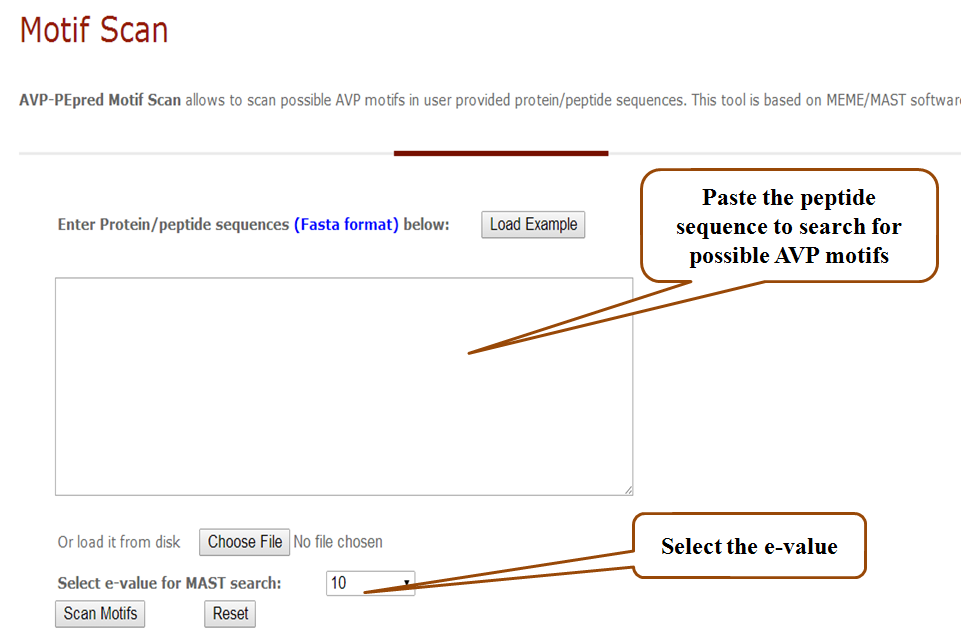
b) Motif finder
This tool finds the possible AVP motifs in the given peptide sequence. These motifs are extracted using the MEME/MAST tool (Bailey, Boden et al. 2009).
c) Property calculator
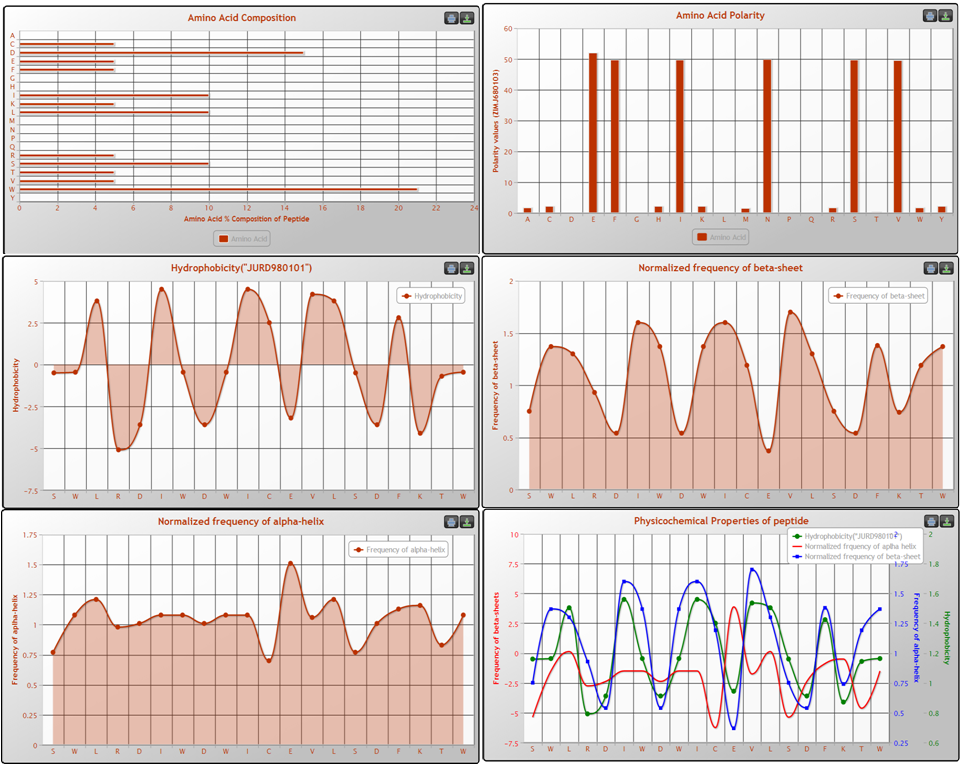
Users can visualize the physicochemical properties of their input peptides by using this tool. The input is a peptide sequence. User can submit and can obtain graphical representation for physicochemical properties such as charge, disorder, flexibility, amino acid composition, and hydrophobicity etc.
d) AVP-PEpred BLAST
AVP-PEpred provides the user with the facility of scanning the existing databases: AVPdb, HIPdb and Uniprot to check if sequences similar to the the user provided peptides have been reported or not. The BLAST output against AVPdb is displayed as shown below. The output is similar for HIPdb and Uniprot.
e) AVP-PEpred Map
The MAP tool is used to fetch the perfectly matching peptides available in the existing databases which map against a user provided protein sequence. It tells as to how many peptides against the user provided protein sequence have been reported earlier.
f) Fragmenter
If a user is having a bigger protein sequence and wishes to find the possible AVP candidates from it, user can use this tool to chop their protein sequence in fragments of desired length and overlaps. The fragments generated at this step can be further given as input for prediction.

 -Database of antiviral peptides.
-Database of antiviral peptides.