
 |
 |
Human Papillomaviruses and Carcinoma
Human papillomaviruses (HPVs) are the small circular double-stranded DNA viruses known to cause diverse carcinomas including cervical, head and neck cancer, vulval, penile etc. It belongs to the papillomaviridae family, taxonomically classified into distinct genera: Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Mupa and Nupa. Persistent infection of high-risk HPVs (HR-HPVs) is the main etiological factor in cancer progression. Despite various efforts, there is no effective treatment and therapeutic solution is available to eradicate HPV mediated carcinomas.
Biomarkers
HPV infection and associated consequences are valuable determinants of multistage neoplastic progression. In this context, there are alternative biomarkers, which could discriminate latent infection with high-grade precursor lesion and eventually cancer. Biomarkers pertinent to HPV mediated diseases are mainly viral DNA integration, viral methylation patterns, and cellular microRNA (miRNAs) expression. These are very crucial factors in cancer progression.
HPVbase Overview
Despite of numerous intensive experimental studies in the field, there is a paucity of computational resources with a unique focus on cancer progression and therapeutically potential biomarkers. Moreover, it is still unclear and less known about the viral mediated processes in different disease conditions.
Hence, it is most important and necessary to have a proper multi-comparative platform of these specific biomarkers. Here, the aim of HPVbase is to provide a web-based resource of the extensively cross-analyzed different biomarkers and genomic information. Additionally, Knowledgebase also serves explored view of different etiological events of cancer progression. Thus, in turn this exhaustive knowledgebase and tools promises to be precious for the assessment of efficacious biomarkers. Finally, combined impact of multiple events can be utilized for the future prevention strategies and therapeutics.
The HPVbase is a first comprehensive web-based, HPV knowledgebase to provide highly curated clinical resource to research community for the effective analysis and assessment of viral and cellular cancer biomarkers. These could improve the reliability of cancer screening and prevention. It has well-designed user interface for the interactive visualization and evaluation. This integrated, multi-comparative platform could facilitate reliable cancer diagnostics and prognosis.
HPVbase is freely available at http://crdd.osdd.net/servers/hpvbase/.
The home page (Figure 1) of HPVbase provides you highly interactive ways to navigate website. It is divided in different sets based on biomarkers, each section represent individual biomarker. Furthermore, home page also includes basic overview and key events in cancer progression. It also includes notification and recent updates area.
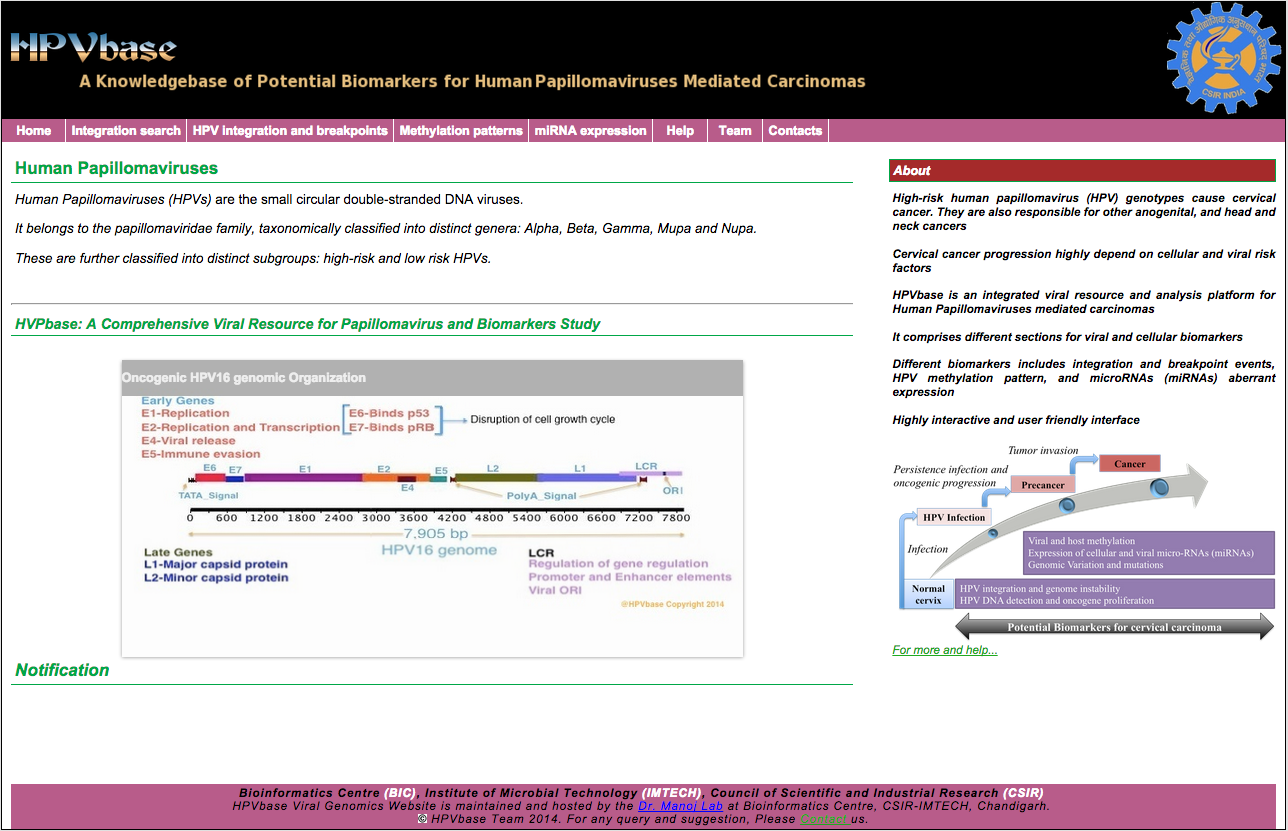
HPVbase Navigation Panel
It provides navigation to all pages using distinct tabs (Figure 2). Different callouts describes individual biomarkers and feature links.

HPV Integration and Breakpoints
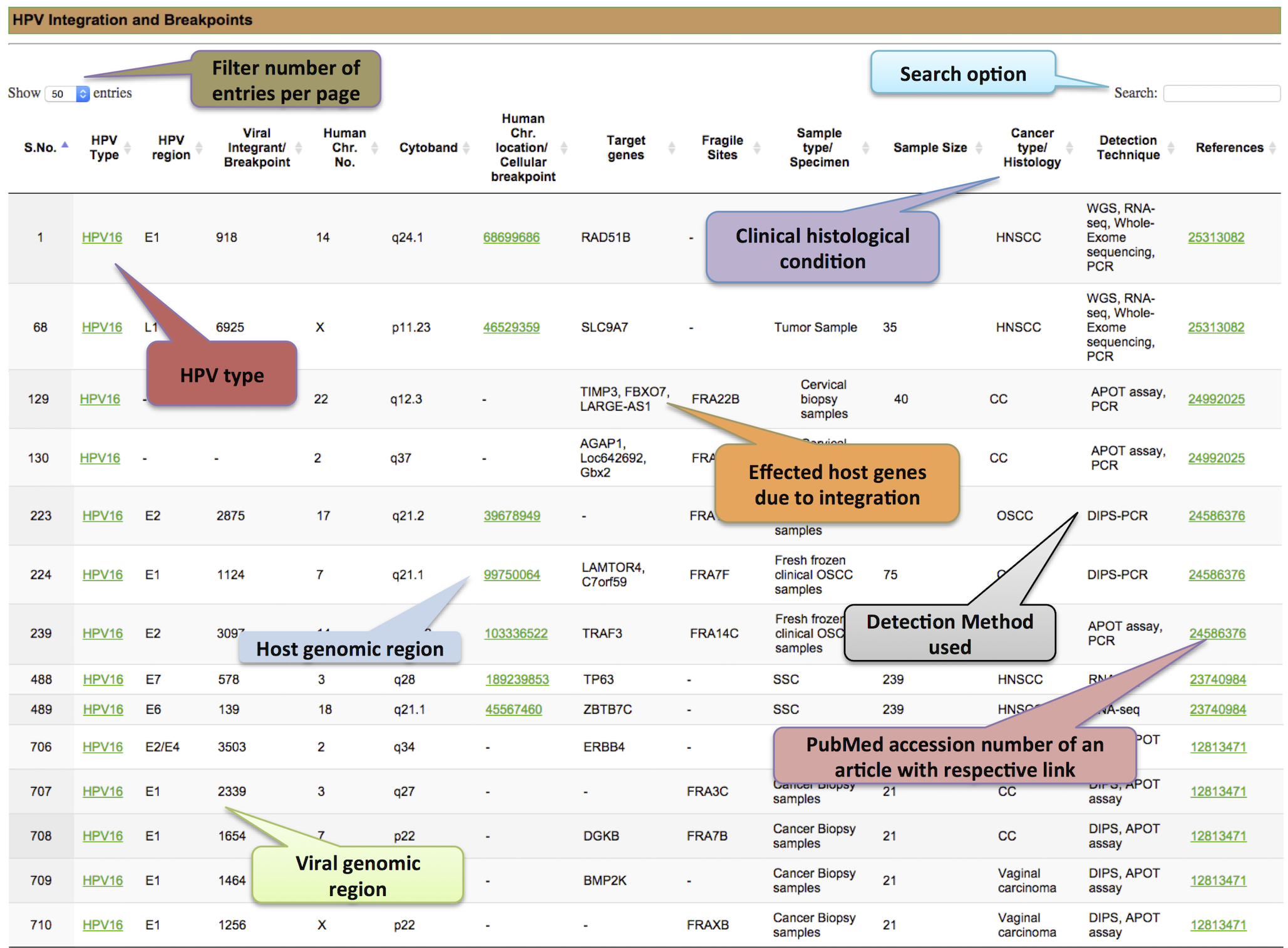
The infection and integration of HPVs is a well-known factor and event in the development of cancer. However, complete knowledge and understanding of integration mechanism is still unclear. An inclusive HPV integrant and breakpoints browser were designed to provide straightforward analysis and clinical interpretations. It comprises of clinically significant 1257 integrants and integration sites from HPV types i.e. 16, 18, 31, 33 and 45 associated with distinct histological conditions. It is represented in both the forms browser and tabular (Figure 3 and 4 respectively).
This allows you to find complete information like viral and host integration site, HPV16 location and genomic region, chromosomal coordinates from human genome, cytoband, target genes, fragile site information, specimen source, cancer histology, detection techniques. By selecting any colored block corresponding to integrant you can find existing analysis and clinical knowledge. Above all, it can be used to perform comparative analysis with new experimental data related to HPV integrant.

HPV Methylation Patterns
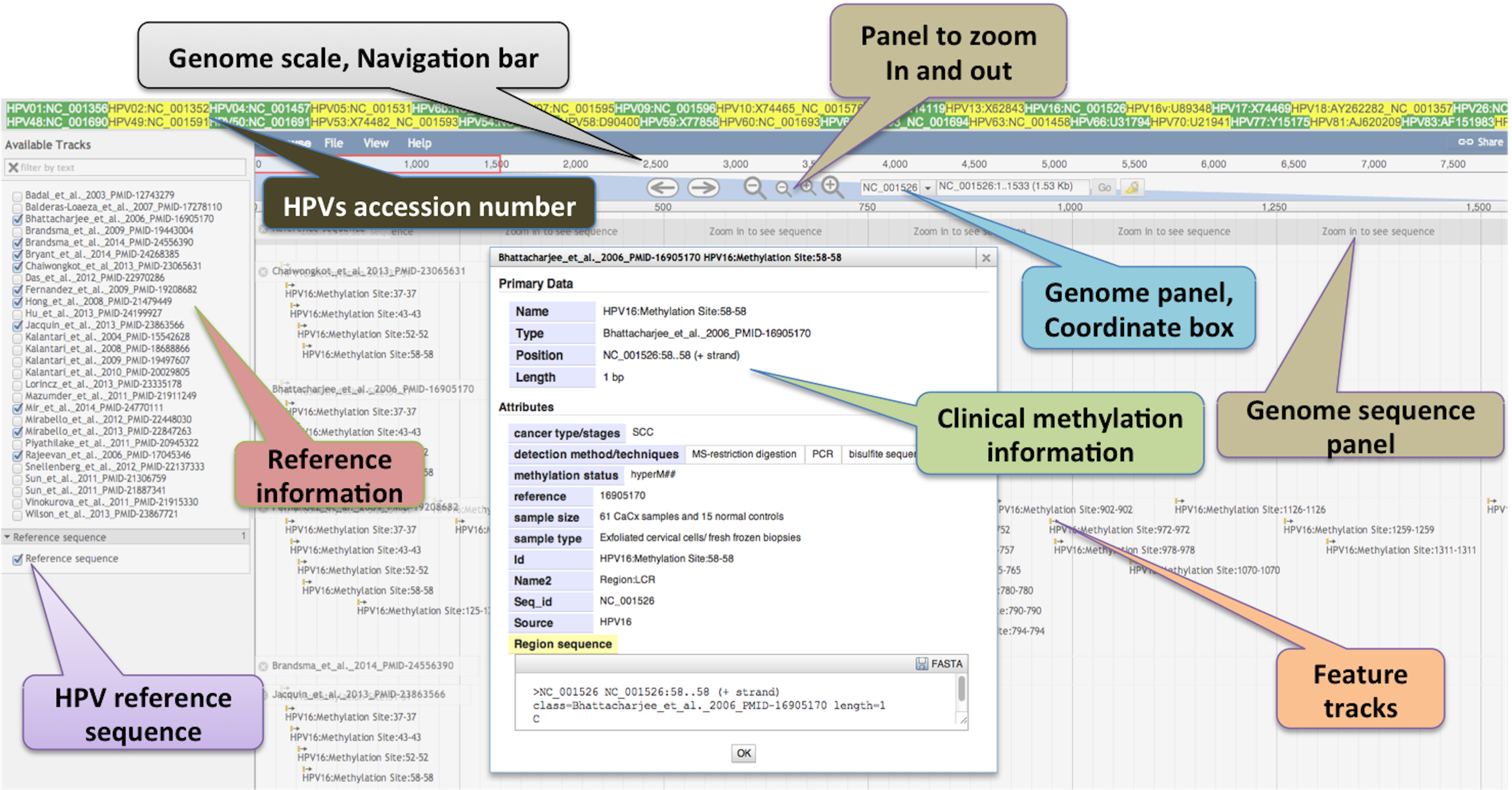
Methylations play a crucial role in the HPV transcriptional modulation. Assorted cancer studies have advocated an association between CpG methylation patterns and the carcinogenic development. The quantitation of HPV DNA methylation may accelerate diagnosis and prognosis of cancer. Our study provides major quantitative HPV DNA methylation observations together and the probable combination of possible CpG methylation sites that could be used to discriminate normal and cancerous progressions. Here we have analyzed and cataloged comparative status of 705 major quantitative HPV DNA methylation observations distributed in 5 distinct HPV genotypes from higher to lower in numbers namely HPV 16 (481), HPV 18 (113), HPV45 (66), HPV 31 (34) and HPV 33 (11). It could provide a comprehensive base for comparative examination between distinctive features and cancers, which in turn facilitate advancement in clinical screening tests.
Cellular miRNAs Aberrant Expression
The aberrant expression of cellular miRNAs influence pathogenesis of cancers. It usually affects various molecular processes such as apoptosis, cell proliferation, morphogenesis, human tumorogenesis, and chromatin modifications. We have developed and integrated computational resource to facilitate strong comparative platform to investigate and explore miRNAs as the efficacious biomarkers in cancer progression. We have curated and compiled clinically significant aberrant expression profile of 338 miRNAs including their target genes from distinct carcinomas. Expression profile of these miRNA can be utilized for the discrimination between normal v/s tumor tissues thus can be used as prognostic marker for aggressiveness of cancer.
User can search different aberrant expression profile using keywords such as miRNAs name, miRNAs ids, cytoband information etc. using search query box.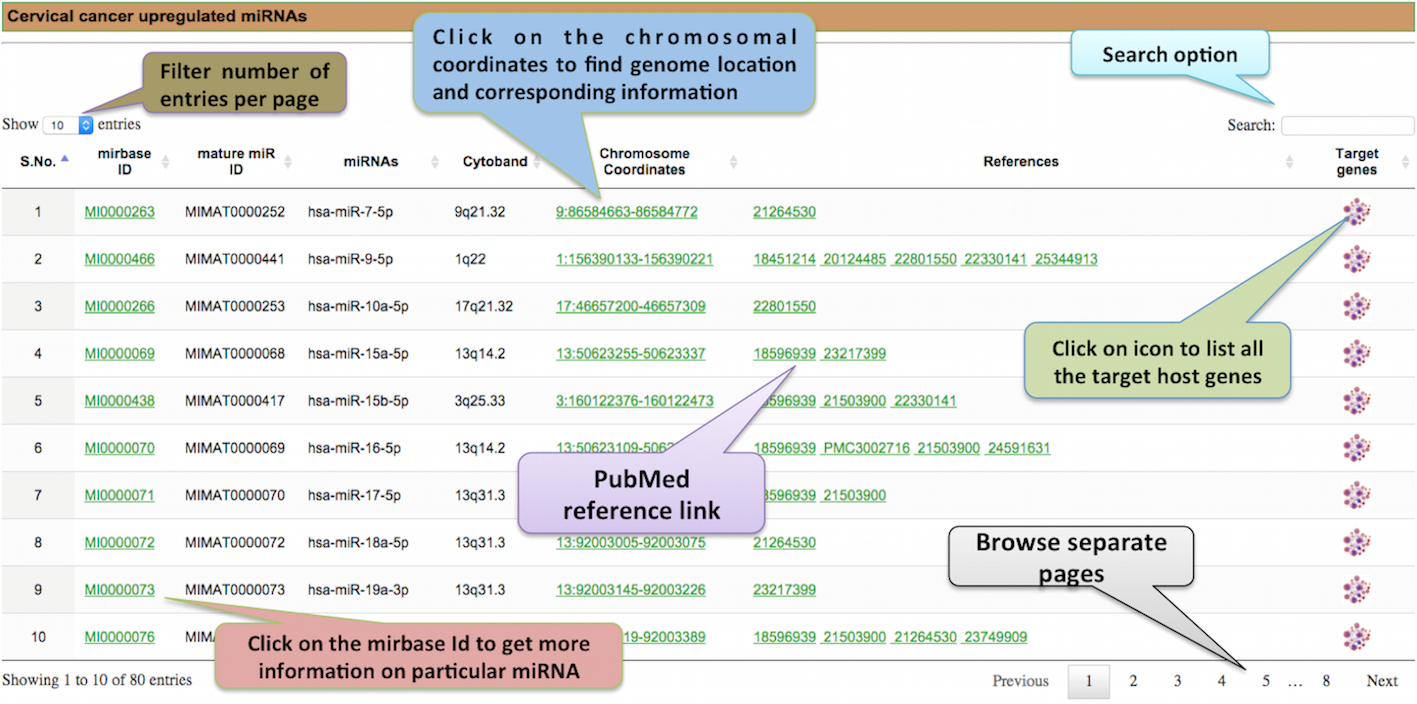
 HPVbase Team 2014. For any query and suggestion, Please
HPVbase Team 2014. For any query and suggestion, Please